How to operate a drone? This seemingly simple question opens a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to efficient surveying and inspection. Mastering drone operation isn’t just about pushing buttons; it’s about understanding the technology, adhering to safety protocols, and respecting legal regulations. This guide provides a structured approach, covering everything from pre-flight checks and basic controls to advanced techniques and legal compliance, ensuring a safe and successful drone piloting experience.
We will delve into the intricacies of drone controls, exploring various flight modes and maneuvering techniques to achieve precise and stable flight. Furthermore, we’ll cover essential camera operation, allowing you to capture stunning aerial imagery. Legal considerations and maintenance procedures will also be addressed, providing a holistic understanding of responsible drone ownership and operation.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures

A thorough pre-flight check is crucial for safe and successful drone operation. This involves inspecting the drone’s components, assessing weather conditions, and understanding emergency procedures. Neglecting these steps can lead to accidents and damage.
Drone Pre-Flight Inspection
Before each flight, meticulously inspect your drone. This ensures all components are functioning correctly and minimizes the risk of malfunctions.
| Component | Inspection Item | Acceptable Condition | Unacceptable Condition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Visual inspection for cracks or damage | No cracks, chips, or bends; securely fastened | Cracks, chips, or bends present; loose or missing propellers |
| Battery | Voltage level and physical condition | Sufficient voltage; no visible damage or swelling | Low voltage; visible damage or swelling |
| Camera | Lens clarity and gimbal functionality | Lens is clean and clear; gimbal moves smoothly | Lens is dirty or scratched; gimbal is stiff or malfunctioning |
| Airframe | Structural integrity and overall condition | No visible damage or cracks; all parts securely attached | Visible damage, cracks, or loose parts |
| Radio System | Signal strength and controller functionality | Strong signal; all controls respond accurately | Weak or intermittent signal; unresponsive controls |
Weather Considerations
Adverse weather significantly impacts drone flight safety. Strong winds, heavy rain, or low visibility can cause loss of control or damage to the drone.
- High winds (above 15 mph): Increased risk of being blown off course or experiencing uncontrolled movements.
- Heavy rain or snow: Can damage electronic components and reduce visibility.
- Fog or low visibility: Reduces the pilot’s ability to see the drone and its surroundings.
- Lightning storms: Significant risk of electrical damage to the drone and potential harm to the operator.
Emergency Procedures
Knowing how to react in emergencies is crucial. A loss of signal or malfunction requires immediate action to mitigate damage or injury.
- Loss of Signal: Immediately activate the Return-to-Home (RTH) function, if available. If RTH fails, visually locate the drone and attempt a manual landing.
- Malfunction: If the drone starts behaving erratically, attempt to regain control using basic maneuvers. If this fails, activate RTH or initiate a controlled descent, prioritizing safety.
Safe Launch and Landing Procedures
Proper launch and landing techniques ensure the safety of your drone and the surrounding environment.
- Launch: Choose a clear, open area away from obstacles. Gently lift the drone, ensuring propellers clear the ground. Then, initiate a controlled ascent.
- Landing: Select a level landing spot. Initiate a slow, controlled descent, maintaining visual contact with the drone. Gently lower the drone to the ground.
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Mastering drone controls is essential for safe and effective flight. This section explains the functions of the control sticks, various flight modes, and techniques for precise maneuvering.
Drone Controller Functions

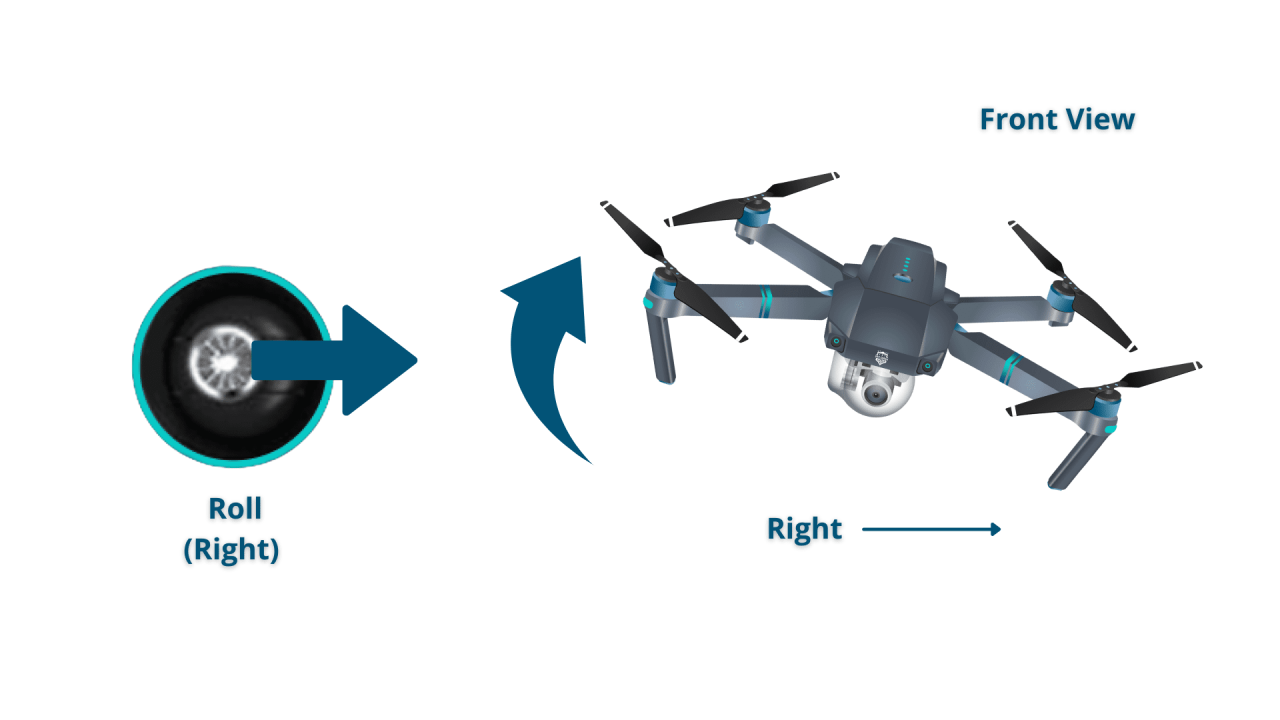
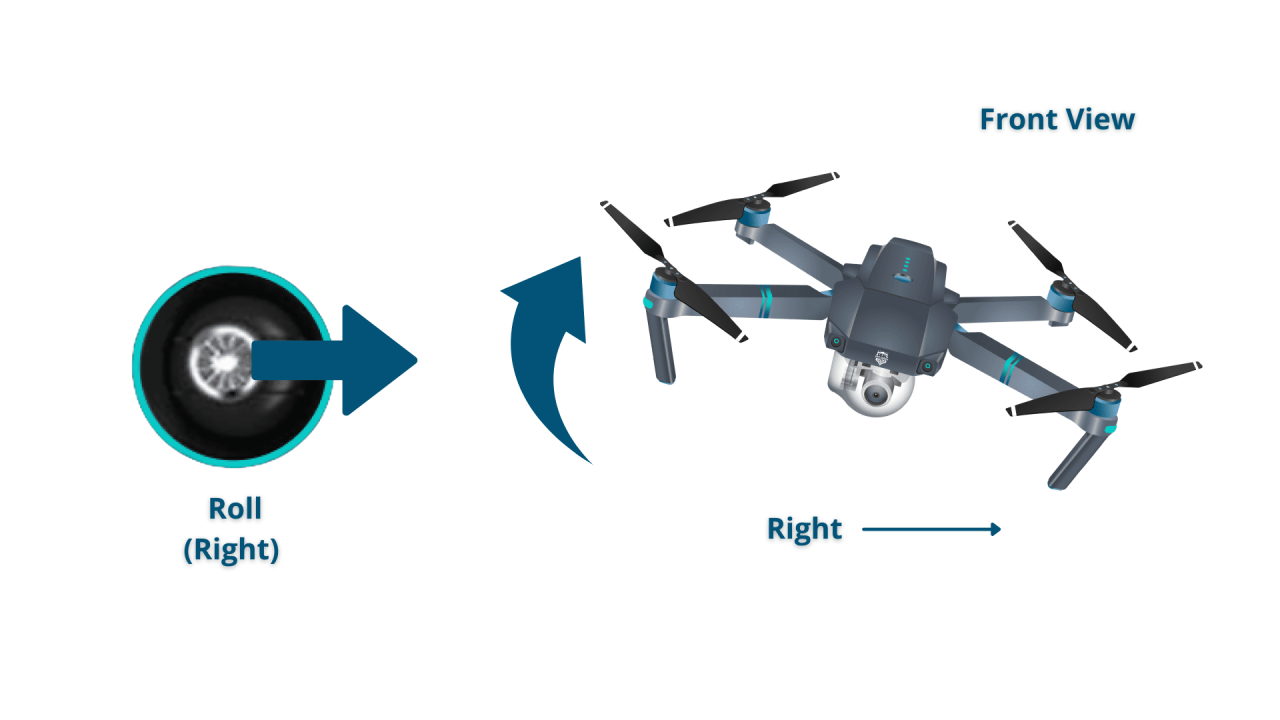
Standard drone controllers typically feature two joysticks. The left stick controls the drone’s altitude and direction, while the right stick manages its pitch and yaw.
- Left Stick (Throttle/Yaw): Vertical movement controls altitude. Horizontal movement controls yaw (rotation).
- Right Stick (Pitch/Roll): Forward/backward movement controls pitch (nose up/down). Left/right movement controls roll (tilting).
Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and stability, adapting to diverse flight situations.
- Altitude Hold: Maintains a constant altitude, simplifying horizontal movement.
- GPS Mode: Uses GPS signals for precise positioning and stability, ideal for longer flights and complex maneuvers.
- Attitude Mode: Provides more direct control over the drone’s movement, suitable for experienced pilots.
- Sport Mode (if available): Increases responsiveness and speed, best used in open areas with no obstacles.
Precise Maneuvering Techniques
Smooth and precise control is crucial for professional-looking footage and safe flight.
- Hovering: Maintaining a stable position in the air requires delicate joystick control and adjustment.
- Smooth Transitions: Avoid abrupt movements by using gentle and gradual joystick inputs.
- Accurate Positioning: Practice precise movements to place the drone exactly where you need it.
Navigating Challenging Environments
Windy conditions and obstacles require specific techniques to maintain control and safety.
- Windy Conditions: Adjust your flight plan to account for wind direction and strength. Fly into the wind during takeoff and landing for increased stability.
- Obstacles: Maintain a safe distance from obstacles. Use the drone’s camera to carefully assess your surroundings and plan your flight path accordingly.
Drone Camera Operation and Photography/Videography
Capturing stunning aerial footage involves understanding camera settings, composition, and creative shot techniques. This section covers the essential aspects of drone photography and videography.
Camera Settings
Drone cameras offer various settings to control image quality and creative effects.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning to navigate safely and effectively is crucial, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques. Ultimately, responsible and skillful drone operation ensures both safety and successful flights.
- ISO: Controls the camera’s sensitivity to light, affecting image noise.
- Shutter Speed: Determines how long the camera’s sensor is exposed to light, impacting motion blur.
- Aperture: Controls the amount of light entering the camera lens, affecting depth of field.
- White Balance: Adjusts the color temperature of the image to ensure accurate colors.
- Resolution and Frame Rate: Determine the image quality and smoothness of video footage.
Composition and Framing
Effective composition enhances the visual appeal of aerial shots. The rule of thirds, leading lines, and symmetry are key compositional elements.
- Rule of Thirds: Placing key elements along imaginary lines dividing the frame into thirds.
- Leading Lines: Using lines to guide the viewer’s eye through the image.
- Symmetry: Creating balanced and visually pleasing images using symmetrical elements.
Creative Shot Techniques
Drones unlock unique perspectives and creative possibilities.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning how to navigate safely and effectively is crucial, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques. Ultimately, proficient drone operation requires practice and a solid understanding of the regulations and safety guidelines.
- Unique Angles: Capture shots from unusual angles, showcasing perspectives unavailable from ground level.
- Dynamic Movement: Incorporate smooth camera movements like pans, tilts, and orbits to add dynamism to your footage.
- Aerial Tracking Shots: Follow moving subjects from above, providing dynamic and engaging perspectives.
Capturing High-Quality Aerial Media
Producing high-quality aerial photos and videos involves careful planning and post-processing.
- Pre-flight planning: Scout your location, plan your shots, and check weather conditions.
- Optimal lighting: Shoot during the golden hour (sunrise and sunset) for soft, warm light.
- Post-processing: Use editing software to enhance color, contrast, and sharpness. Correct any distortions or imperfections.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Operating a drone responsibly requires understanding and adhering to local regulations. This includes registration, airspace restrictions, and privacy considerations.
Drone Regulations
Drone laws vary by region. It’s crucial to research and comply with the specific regulations in your area. Failing to do so can result in fines or legal action.
- Registration: Many regions require drone registration with the relevant aviation authority.
- Airspace Restrictions: No-fly zones exist near airports, military bases, and other sensitive areas.
- Permits and Licenses: Specific permits may be needed for commercial drone operation or flights in restricted airspace.
- Privacy Laws: Respect individuals’ privacy and avoid filming people without their consent.
- Operational Limits: Adhere to limitations on flight altitude, distance, and speed.
Drone Registration and Permits
Registering your drone is often mandatory. This allows authorities to track drone operators and ensure compliance with regulations. Certain commercial operations might also require specific permits or licenses.
Airspace Restrictions
Identifying and avoiding no-fly zones is critical. Use online resources and apps to check for restricted airspace before each flight.
Privacy and Data Security
Respecting people’s privacy is paramount. Avoid filming individuals without their consent, and ensure you comply with data protection laws regarding any footage captured.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting skills extend the lifespan of your drone and prevent unexpected issues. This section Artikels a maintenance schedule and common troubleshooting steps.
Drone Maintenance Schedule
A regular maintenance schedule ensures your drone remains in optimal condition.
| Task | Frequency | Procedure | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clean Propellers and Airframe | After each flight | Use a soft cloth and mild detergent to clean dirt and debris. | Avoid harsh chemicals. |
| Inspect Propellers for Damage | Before each flight | Check for cracks, chips, or bends. Replace damaged propellers. | Replace immediately if damage is detected. |
| Check Battery Voltage and Condition | Before each flight | Use a battery checker to ensure sufficient voltage. Inspect for swelling or damage. | Store batteries properly to maintain their lifespan. |
| Software Updates | As released | Check for and install firmware updates from the manufacturer. | Updates often include bug fixes and performance improvements. |
| Inspect Gimbal and Camera | Weekly | Check for proper functionality and clean the lens. | Use a microfiber cloth to clean the lens. |
Common Drone Problems and Solutions
Understanding common issues and their solutions helps maintain your drone’s functionality.
- Low Battery: Charge the battery fully. Consider using higher-capacity batteries for longer flight times.
- Poor Signal: Check for interference, move to an open area, and ensure the controller’s batteries are fully charged.
- Gimbal Malfunction: Check for physical obstructions and try recalibrating the gimbal.
- Propeller Damage: Replace damaged propellers immediately.
Replacing Damaged Parts
Replacing damaged parts is often straightforward, but always follow the manufacturer’s instructions.
Proper Storage and Transportation
Proper storage and transportation protect your drone from damage and extend its lifespan. Use a protective case during transport, and store the drone in a cool, dry place.
Advanced Drone Techniques
This section explores advanced techniques for enhancing your drone operation and capturing professional-quality footage.
Waypoint Missions
Waypoint missions allow you to program the drone to fly a predetermined path, automating complex shots.
Drone Cinematography
Drone cinematography combines flight skills with storytelling techniques to create engaging visual narratives.
Advanced Features, How to operate a drone
Modern drones often include features like obstacle avoidance and return-to-home (RTH) for increased safety and convenience.
Sensor Calibration
Regular sensor calibration ensures the drone’s sensors provide accurate data, leading to smoother and more stable flights.
Successfully operating a drone requires a blend of technical skill, responsible awareness, and adherence to regulations. From understanding pre-flight safety procedures to mastering advanced flight maneuvers and post-processing techniques, this guide provides a solid foundation for your drone piloting journey. Remember, safe and responsible operation is paramount, ensuring both your safety and the safety of those around you. Embrace the possibilities, fly safely, and enjoy the breathtaking perspectives that drone technology offers.
FAQ Guide: How To Operate A Drone
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones are available for beginners. Look for models with features like GPS stabilization, obstacle avoidance, and return-to-home functionality.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model and flight conditions. Expect flight times ranging from 15 to 30 minutes, often less in windy conditions or with heavier camera payloads.
What happens if my drone loses connection?
Most modern drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function. If signal is lost, the drone will attempt to return to its takeoff point. Always fly within visual line of sight to mitigate risk.
Can I fly my drone anywhere?
No. Drone operation is subject to various regulations and airspace restrictions. Check local laws and regulations before flying, and always avoid restricted areas.